Melatoninis widely studied for its role in regulating sleep, with some evidence suggesting broader effects on health and cognition. Let us take a closer look at the marvels behind melatonin’s powerful effects on the brain and body and gain insight into how it can optimize cognitive performance and promote restful sleep.
Melatonin as a Nootropic Supplement
When we consider melatonin a nootropic, it has been investigated for potential cognitive effects. Though it is most famous for its vast benefits in sleep regulation and maintaining sleep-wake cycles, melatonin is quickly recognized for its potential to boost brain function. Some studies suggest melatonin may have neuroprotective properties and a role in memory processes, though evidence in humans is limited.
As we examine its nootropic features more closely, we find that it offers a unique pathway to sharpening cognitive skills while nurturing overall well-being. By supporting circadian rhythms and sleep quality, it may indirectly improve focus and daytime performance.
Mechanism of Action
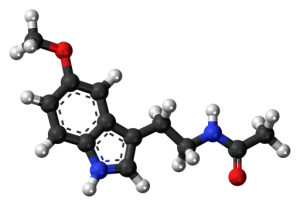
As the supplement is easily recognized as a “sleep hormone,” its mechanism of action is also linked with our pineal glands. Melatonin is a natural hormone that is present in the pineal gland of our brain. Its primary function is to monitor the sleep-wake cycle and ultimately contribute towards improving it. This function signals the body when it’s time to wind down and rest. The natural level of melatonin rises in response to darkness, which is an indicator for our bodies that it’s nighttime and we should prepare for sleep. [R]
Image source: Wikipedia
Melatonin also functions as an antioxidant, helping to neutralize free radicals that contribute to cellular aging. It searches for and collects free radicals that damage cells and contribute to aging. It also plays a vital role in overall health by synchronizing our internal body clock with the natural order. This feature improves our sleep quality and protects our cells from aging due to stress.
Melatonin’s Impact on Sleep
Melatonin is probably best known for its effects on sleep. Let us try to understand the complicated relationship between this natural hormone and our circadian rhythm. It plays a critical role in signaling to our body that it’s time to leave everything aside and prepare for rest. This signal of winding down aligns with our internal clock and helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle. Moreover, it promotes a sense of calm and readiness for slumber.
The powerful supplement not only aids in falling asleep but also affects the quality of our rest. It may influence sleep architecture and improve overall sleep efficiency in some individuals. Thus, with the help of melatonin, individuals awaken feeling refreshed and revitalized, ready for carpe diem (seizing the day). [R]
Benefits: Melatonin as a Game-Changer
While melatonin is primarily known for regulating sleep-wake cycles, its benefits extend far beyond improving sleep quality. Its vast array of benefits include:
- It is best known for combating sleep disorders such as insomnia. It helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle, making it easier to fall and stay asleep. So, it’s best feature is improving the quality of our sleep. [R]
- It alleviates symptoms of jet lag by helping to adjust the body’s internal clock to a new time zone. This makes it a popular supplement for travelers crossing multiple time zones. [R]
- It protects the eyes from damage caused by free radicals. It also helps prevent age-related macular degeneration and other eye diseases. [R]
- Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is a type of depression that occurs at certain times of the year, usually in the winter. It regulates mood and improves symptoms of SAD by aligning the body’s circadian rhythms with natural light cycles. [R]
- Some studies suggest it may influence blood pressure, cholesterol, and inflammation, but more research is needed. [R]
- It plays a role in supporting the immune system. It enhances immune response and helps the body fight off infections. [R]
- Some small studies suggest it may help with tinnitus symptoms, possibly by improving sleep and reducing anxiety. [R]
- It reduces the frequency and severity of migraines. Its effects on sleep regulation and pain modulation contribute to fewer migraine attacks. [R]
- Early research is exploring it’s role in cancer therapy, but findings are preliminary and not clinically established. [R]
Side Effects
As with any supplement, melatonin may pose potential side effects that individuals should be aware of. While melatonin is generally well-tolerated, some users may experience mild side effects such as dizziness, headaches, or gastrointestinal disturbances. To avoid these issues, starting with a low dosage and monitoring your body’s response is essential.
Ideal Dosage of Melatonin
The recommended dosage varies depending on individual factors like age and sensitivity. Typical studies use doses from 0.5–5 mg, though individual needs vary. It’s best to start low and consult a healthcare professional.
How to Select the Right Melatonin Supplement
When it comes to choosing the right melatonin supplement, discernment is critical. Look for supplements that are third-party tested for purity and potency. Opt for formulations free from artificial additives, colors, and preservatives. Consider your specific needs, whether you require a fast-acting formula or a prolonged-release option.
Conclusion
As we conclude this exploration into melatonin as a nootropic supplement, it becomes evident that its potential goes far beyond just aiding in sleep. The intricate mechanisms of action, its wide-ranging benefits, and compelling user experiences paint a picture of a genuinely versatile cognitive enhancer.
The future holds promise for further innovations in melatonin research, offering exciting possibilities for enhancing mental performance and overall well-being. So, as you venture into the realm of nootropics, remember that melatonin remains best known as a sleep aid, with ongoing research exploring its broader health effects.
FAQs
Is melatonin addictive?
Melatonin is not considered addictive and does not cause physical dependence. It works with your body’s natural sleep cycle to promote restful sleep without altering brain chemistry in a way that leads to dependency. It’s a safe and effective supplement for occasional use.