Sleep is essential for physical recovery, memory consolidation, and immune function. DSIP (Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide) is an experimental neuropeptide studied for its potential effects on sleep and stress responses.
Introduction:
DSIP is a naturally occurring neuropeptide in the nervous system. It was first isolated from rabbit cerebral venous blood in 1977.
DSIP is believed to play a role in the regulation of sleep just like some nootropics for sleep. Some studies suggest that it may have sleep-inducing effects, particularly on the delta rhythm of electroencephalogram (EEG) activity during sleep. Delta sleep-inducing peptide may be involved in modulating the body’s response to stress. It has been investigated for its potential anti-stress and anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing) effects.
DSIP has been studied for its immunomodulatory effects. It may influence the immune system and participate in the regulation of inflammatory processes. Moreover, Some research indicates that it may have analgesic (pain-relieving) effects.
What is DSIP: Product Information
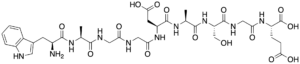
DSIP is a small peptide composed of nine amino acids. The specific sequence of amino acids in DSIP is Trp-Ala-Gly-Gly-Asp-Ala-Ser-Gly-Glu. It was named for its suggested role in regulating sleep patterns. Studies have suggested that Delta sleep-inducing peptide may play a role in promoting delta-wave sleep, which is a stage of deep sleep associated with restorative and rejuvenating processes in the body. The nonapeptide could promote sleep through the induction of slow-wave sleep.
DSIP has been suggested to act as a hypothalamic neuropeptide with potential sleep-inducing properties which may contribute to the regulation of sleep-wake cycles. It may influence the release of hormones involved in the body’s stress response.
Moreover, research has explored the immunomodulatory effects of Delta sleep-inducing peptide. It may play a role in regulating the immune system and influencing inflammatory processes.
Mechanism of Action
DSIP and DSIP-like peptides have been detected in brain, endocrine glands, and peripheral tissues in several species, though its precise distribution in humans remains debated. Here is the sleep onset mechanism of action of the DSIP peptide:
Sleep Modulation: It is a peptide believed to promote delta-wave sleep. Delta wave sleep is a stage of deep sleep associated with restorative and rejuvenating processes in the body. It may interact with pathways involving sleep-promoting mediators such as prostaglandin D2, though exact receptor targets are unclear. {R}
Hormonal Regulation: It has been shown to influence the release of certain hormones, including corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). These hormones are part of the body’s stress response system. It’s ability to modulate these hormones may contribute to its anti-stress and anxiolytic effects. {R}
Neurotransmitter Regulation: It may influence neurotransmitter systems, but specific mechanisms remain uncertain. It could influence the balance of neurotransmitters involved in mood and stress responses. {R}
DSIP Peptide Benefits
Some of the potential benefits associated with DSIP are:
Sleep Regulation:
It is named a sleep peptide for its purported ability to influence sleep structure, specifically promoting delta-wave sleep. It is studied for its potential role in promoting deep, restorative sleep.
Preliminary research suggests DSIP may influence sleep efficiency, though human evidence is limited. {R}
Stress Reduction:
Some studies suggest that it may have anti-stress and anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing) effects. It could potentially modulate the body’s response to stress and contribute to a sense of relaxation. {R}
Immune System Modulation:
It has been investigated for its immunomodulatory effects. It may play a role in regulating the immune system, potentially influencing inflammatory responses. {R}
Pain Modulation:
Preliminary studies hint at possible analgesic effects, though findings are inconsistent. It could potentially affect the perception and processing of pain signals. {R}
Hormonal Regulation:
DSIP may influence the release of certain hormones, including corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). These hormones are involved in the body’s stress response. {R}
Recommended Dosage
If you are suffering from chronic insomnia and are new to using DCIP, start with 100mcg and up the dosage to 200mcg until you are satisfied with the effect. Consult healthcare professional before starting any regimen.
In research settings, DSIP is typically handled in lyophilized form and reconstituted for study. It is not approved for self-administration. When it comes to self-injection, it’s highly important to educate yourself and be careful. Peptides are usually injected intramuscularly or subcutaneously.
Side Effects
Side effects are not well-documented due to limited research, but the ones that may show up could be related to its influence on sleep, hormonal regulation, and other physiological processes. General considerations include:
Sleep-related effects:
Changes in sleep patterns could potentially occur, and individual responses to Delta sleep-inducing peptide may vary. This could include alterations in sleep duration or sleep architecture.
Hormonal effects:
It may influence the release of certain hormones, including those involved in the stress response. This could potentially lead to hormonal imbalances, although the specific effects are not well-established.
Is DSIP Legal?
DSIP is not FDA-approved. It is available only for research purposes and not for human consumption.
Conclusion:
Endogenous peptides like DSIP are among several humoral factors that may influence sleep regulation. Delta sleep-inducing peptide is a nonapeptide that could promote sleep through the induction of slow-wave sleep in chronic insomniac patients and produce higher sleep efficiency by affecting the humoral factors involved. DSIP remains experimental. While it shows potential in sleep research, its safety and efficacy in treating insomnia are unproven.